物理科
- 課程宗旨
本課程的宗旨是讓學生:
- 對物理世界產生興趣, 保持對物理世界的好奇心和求知欲;
- 建構及應用物理學的知識, 鑑賞物理科學與其他學科之間的關係;
- 藉與物理學相關的情境了解和鑑賞科學的本質;
- 掌握進行科學探索的技能;
- 培養科學性、明辨性和創造性的思考能力, 以及在單獨或在與他人協作的情況下, 解決與物理學有關問題的能力;
- 理解有關物理學議題的科學語言, 並能與他人交流觀點;
- 在與物理學有關的議題上, 作出明智的判斷和決定;
- 關注物理學對社會、道德、經濟、環境和科技的影響, 以及養成負責任的公民態度。
- 中學畢業後出路的銜接
高中學制提供多條路徑銜接專上教育及就業,使每位學生均有機會踏上成功之路。下圖說明可行的路徑:
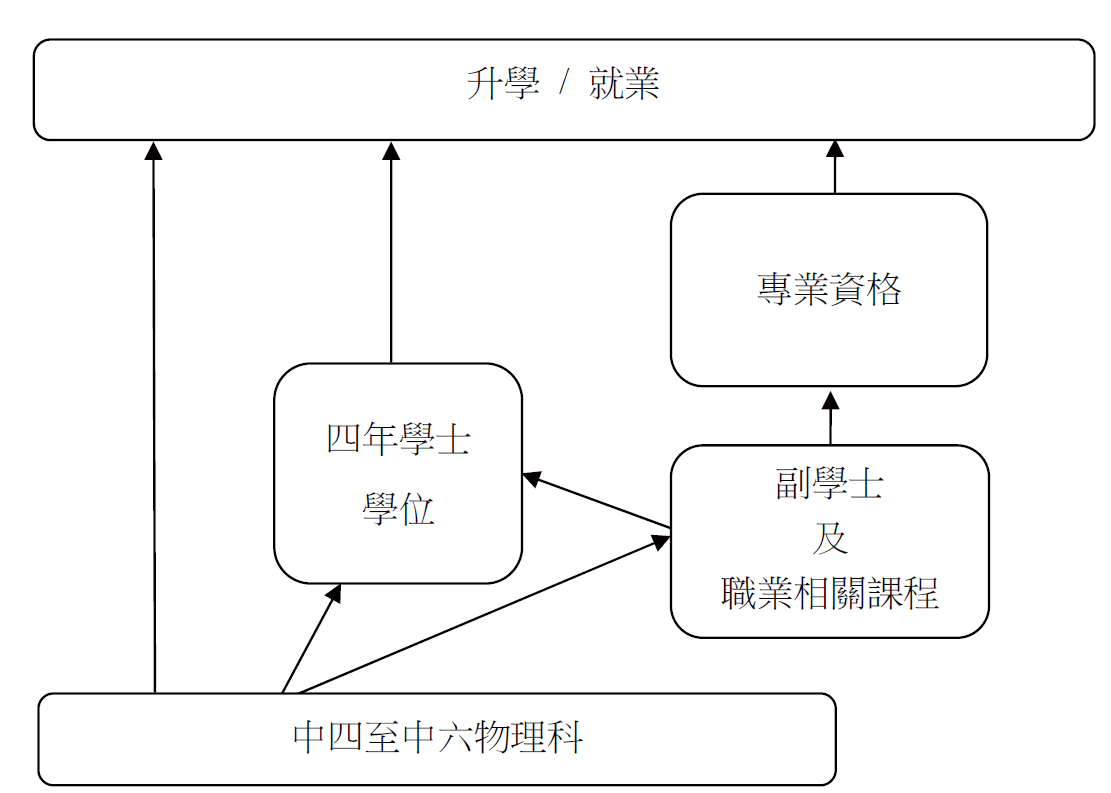
升學及就業的各種路徑
- 課程結構及組織
|
必修部分
|
|
熱和氣體
|
- 溫度、熱及內能
- 熱轉移過程
- 物態的改變
- 氣體
|
|
力和運動
|
- 位置和移動
- 力和運動
- 拋體運動
- 作功、能量和功率
- 動量
- 匀速圓周運動
- 引力
|
|
波動
|
- 波的本質和特性
- 光
- 聲音
|
|
電和磁
|
- 靜電學
- 電路和家居用電
- 電和磁
|
|
放射現象和核能
|
- 輻射與放射現象
- 原子模型
- 核能
|
|
選修部分
|
|
原子模型
|
- 盧瑟福原子模型
- 光電效應
- 玻爾的氫原子模型
- 粒子或波
- 窺探納米世界
|
|
能量和能源的使用
|
- 家居用電
- 在建築和運輸業中的能源效率
- 可再生和不可再生能源
|
|
探究研習
|
|
物理科探究研習
|
學生必須進行一項探究活動, 解決一個實質問題。
|
- 國家安全教育課程框架
|
物理科 (中四至中六)
|
香港國家安全
教育課程框架
|
|
章節 / 課題
|
學習元素
|
|
放射現象和核能
|
- 明白致電離輻射的潛在危險 性和減少吸收輻射劑量的方 法
- 認識處理放射源的安全措施
- 認識核裂變及核聚變時能量 的釋放
- 認識原子核的連鎖反應
- 在 教 授 「 放 射 現 象 和 核能」時, 讓學生搜集有關使 用 核 能 所 帶 來 的 好 處和潛在風險, 以及核災難事件的資料, 探討使用核能 對 生 態 安 全 和 資 源 安全的複雜影響, 從而認同維護核安全的必要性。
|
了解人類活動 對生態環境的 影響和責任, 明白可持續發 展的需要,認 同維護生態安 全 、 資 源 安全、核安全和 新型領域安全 的必要性
|
|
能量和能源的使用
|
- 認識可再生和不可再生能源 的特徵
- 認識能源的提取、轉移、分 配及使用, 對環境和社會的 衝擊
- 明白溫室氣體對全球暖化的 影響
- 在教授「能量和能源的使用」時, 讓學生透過研習及 分 析 有 關 能 源 與 溫 室氣體相互作用的資料,探討 能 量 和 能 源 等 資 源 的使用對生態的影響, 從而認 同 維 護 生 態 安 全 和 資
源安全的必要性。
|
Physics
- Curriculum Aims
The broad aims of the curriculum are to enable students to:
- develop interest in the physical world and maintain a sense of wonder and curiosity about it;
- construct and apply knowledge of physics, and appreciate the relationship between physical science and other disciplines;
- appreciate and understand the nature of science in physics-related contexts;
- develop skills for making scientific inquiries;
- develop the ability to think scientifically, critically and creatively, and to solve problems individually or collaboratively in physics-related contexts;
- understand the language of science and communicate ideas and views on physics-related issues;
- make informed decisions and judgments on physics-related issues; and
- be aware of the social, ethical, economic, environmental and technological implications of physics, and develop an attitude of responsible citizenship.
- Interface with Post-secondary Pathways
The senior secondary academic structure provides a range of pathways to higher education and the workplace so that every student has an opportunity to succeed in life. Figure below shows the possible pathways.
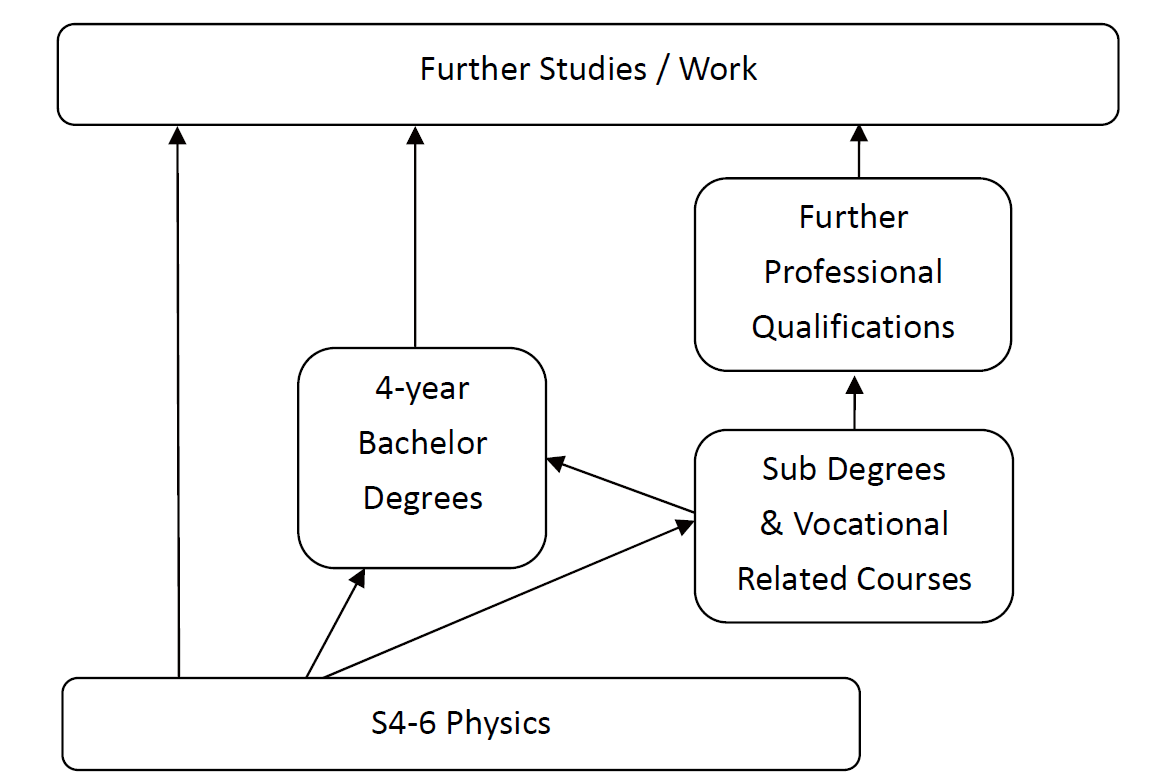
Multiple Pathways to Higher Education and the Workplace
- Curriculum Structure and Organization
|
Compulsory part
|
|
Heat and Gases
|
- Temperature, heat and internal energy
- Transfer processes
- Change of state
- Gases
|
|
Force and Motion
|
- Position and movement
- Force and motion
- Projectile motion
- Work, energy and power
- Momentum
- Uniform circular motion
- Gravitation
|
|
Wave Motion
|
- Nature and properties of waves
- Light
- Sound
|
|
Electricity and Magnetism
|
- Electrostatics
- Circuits and domestic electricity
- Electromagnetism
|
|
Radioactivity and Nuclear Energy
|
- Radiation and radioactivity
- Atomic model
- Nuclear energy
|
|
Elective part
|
|
Atomic World
|
- Rutherford’s atomic model
- Photoelectric effect
- Bohr’s atomic model of hydrogen
- Particles or waves
- Probing into nano scale
|
|
Energy and Use of Energy
|
- Electricity at home
- Energy efficiency in building and transportation
- Renewable and non-renewable energy sources
|
|
Investigative Study
|
|
Investigative Study in Physics
|
Students should conduct an investigation with a view
to solving an authentic problem
|
4. Curriculum Framework of National Security Education
|
Physics (S4-6)
|
Curriculum Framework of National Security Education in
Hong Kong
|
|
Chapter / Topic
|
Learning elements
|
|
Radioactivity and Nuclear Energy
- Radiation safety issues
- Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
|
- Understand the potential dangers of ionizing radiation and ways to reduce absorbed radiation doses
- Recognize safety measures for handling radioactive sources
- Understand the release of energy during nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
- Understanding the chain reaction of atomic nuclei
- In the teaching of “Radioactivity and Nuclear Energy”, let students collect information on the benefits and potential risks of the use of nuclear energy, as well as information on nuclear disaster events, discuss the complex impact of the use of nuclear energy on ecological security and recognise the
necessity of nuclear security
|
Understand the impact of human activities on the ecological environment and our responsibilities, understand the needs of sustainable development,
and recognise the necessity of safeguarding ecological security, resource security, nuclear security and new security domain
|
|
Energy and Use of Energy
- Renewable and non-renewable energy sources
- Impact of energy consumption on the environment
|
- Recognize the characteristics of renewable and non-renewable energy sources
- Recognize the environmental and social impacts of energy extraction, transfer, distribution and use
- Understand the impact of greenhouse gases on global warming
- When teaching “Energy and Use of Energy”, let students explore the impact of the use of energy and energy and other resources on the ecology through studying and analyzing the data on the interaction of energy and greenhouse gases, so as to recognise the necessity of safeguarding ecological security
and resource security,
|

